Outcomes: IR spectra showed five important band on 3105, 2905, 1725, 1699 and 1605 respectively as show in (Fig 2) which were corresponding to (C-H) aromatic and (C-H) aliphaticand also C=O of ester, C=O of amide and C=N of pyridine ring of IVB .that is good support to formation of oxazepine derivatives. The mass fragment ion showed ion peak at. The mass spectra of synthesized target compounds showd molecular ion peaks at 319,329 and 318 in mass spectral which are blelong to the following molecular ion of the synthesized strucutre
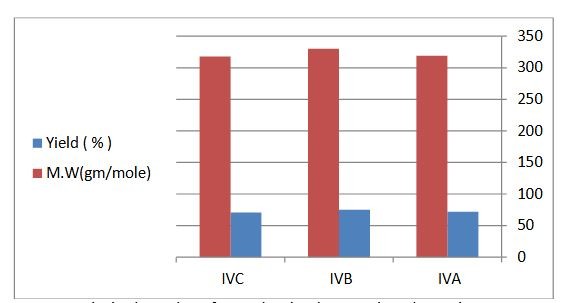
In this project 4 oxazepine compounds formed with different components.
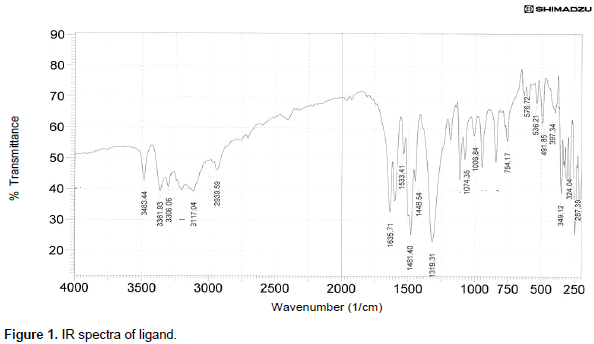
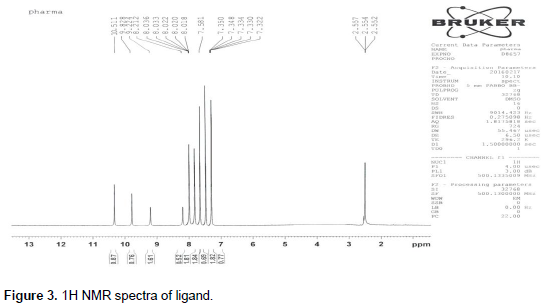
Outcomes: The spectrum reveals well-defined aromatic and aliphatic proton peaks, verifying ligand structure by characteristic chemical shifts and splitting patterns, indicative of clean synthesis and distinct proton environments. 1H NMR spectrum of a ligand, showing multiple proton environments with peaks between 13 to 1 ppm, indicating chemical shifts typical for aromatic and aliphatic hydrogens. The IR spectrum of the ligand shows distinctive peaks for O-H, C-H, and aromatic or carbonyl groups, confirming the presence of multiple functional groups in the molecular structure.
In this project 4 oxazepine compounds formed with different halogens.
Outcomes: Development of biofertilizers, Identification of Bacillus strains with potential applications in agriculture. Analysis of cellulase enzyme production: Identification of bacterial enzymes with potential applications in various industries. Bioremediation strategies: Observed bioremediation approaches using Bacillus strains for cleaning up contaminated soil.
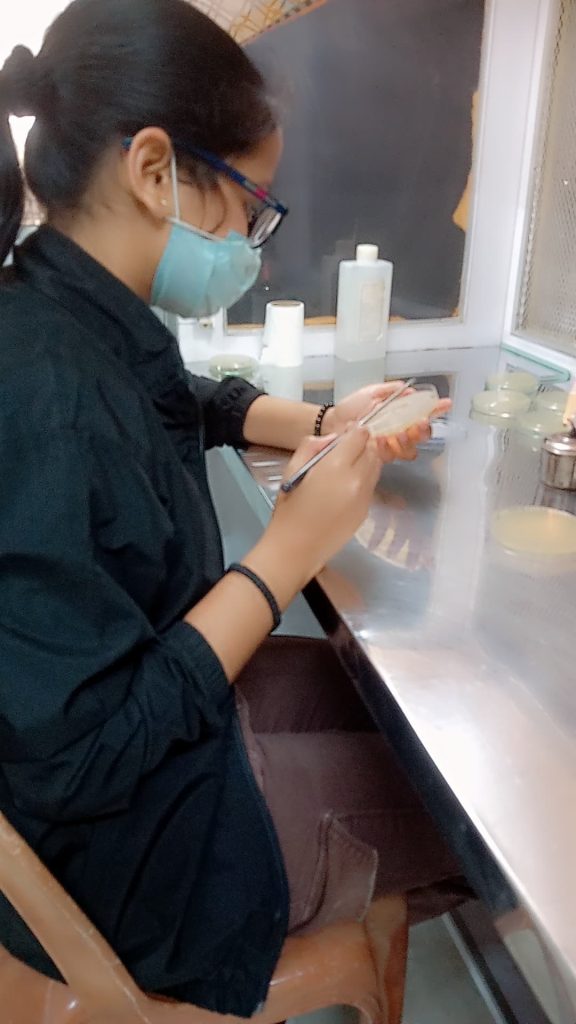
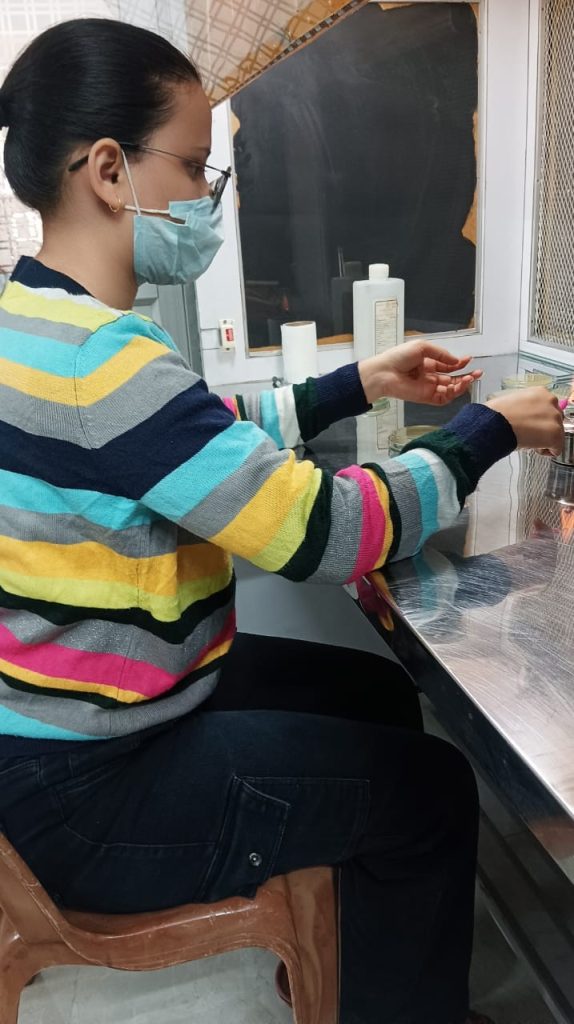
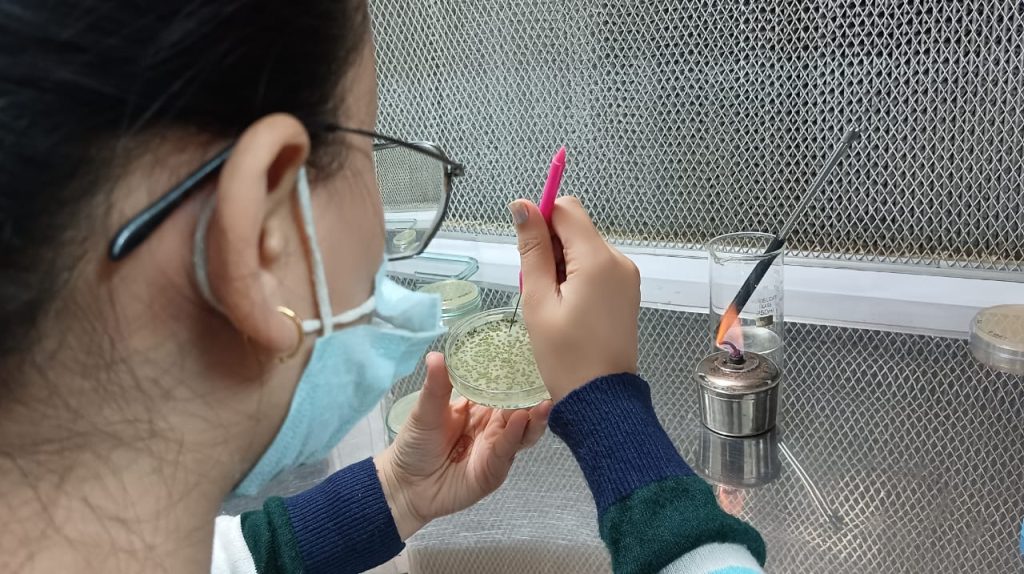



Outcomes: Development of sustainable waste-to-wealth strategies: The study helped in the development of innovative approaches for converting industrial waste into valuable products, such as bioethanol, biochemicals. The research resulted in optimized processes for bioethanol production from industrial waste (Agrowaste), contributing to a more sustainable and renewable energy source. The valorization of industrial waste could lead to reduced waste disposal costs, decreased environmental pollution, and a more circular economy. The Bioethanol was quantified by the spectrophotometric method.
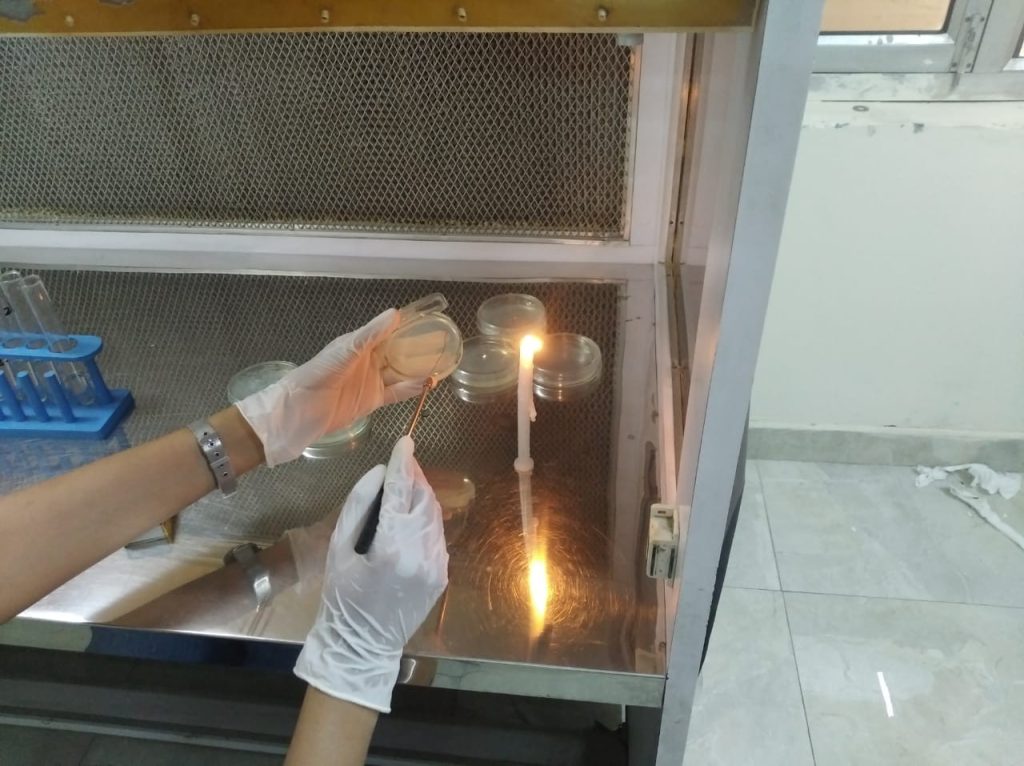
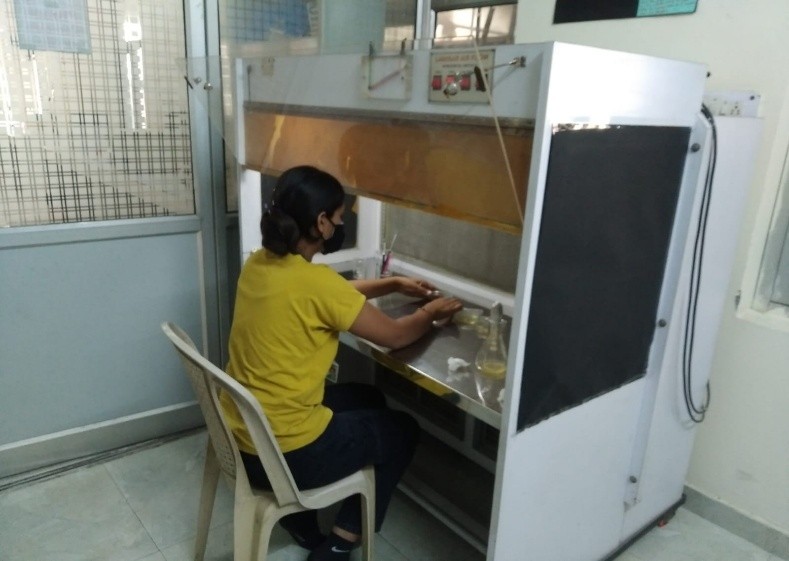
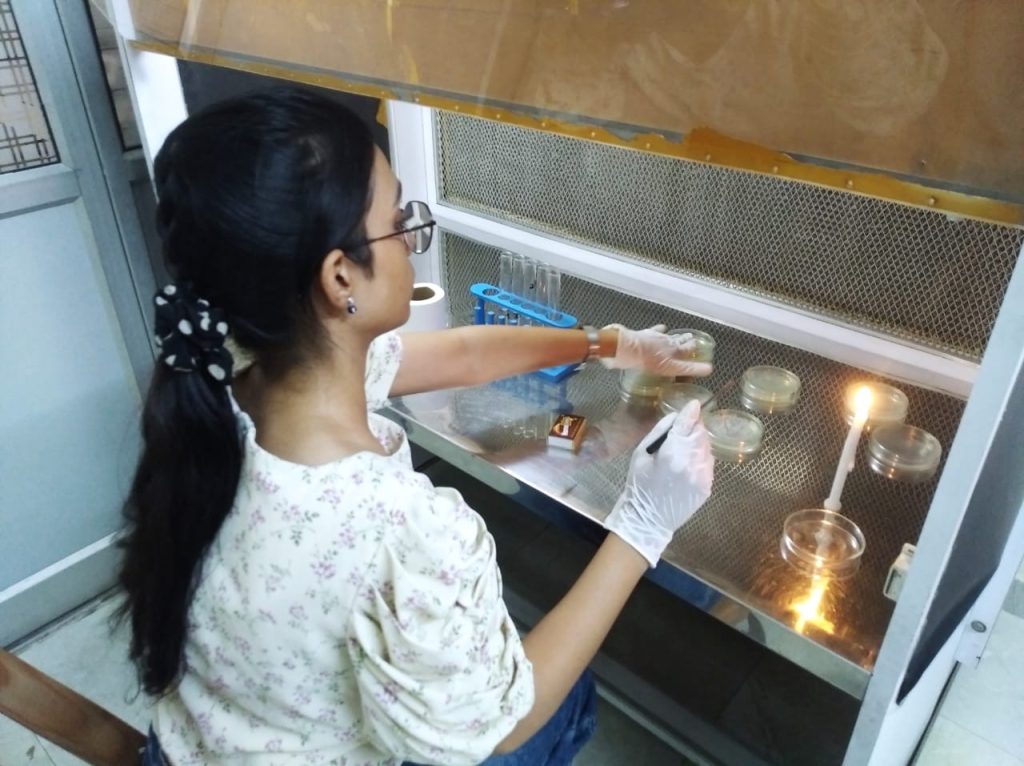



Outcomes: Identification of novel copper-resistant bacterial strains: The study may lead to the discovery of new bacterial strains that can tolerate high levels of copper, which could have potential applications in bioremediation. The research work helped in understanding the mechanisms of copper resistance: The research shed light on the molecular mechanism of absorption of vitamins for culture development of optimised process. Based on our findings the isolated bacterial strains could be used to develop effective bioremediation protocols for cleaning up copper-contaminated industrial waste sites.
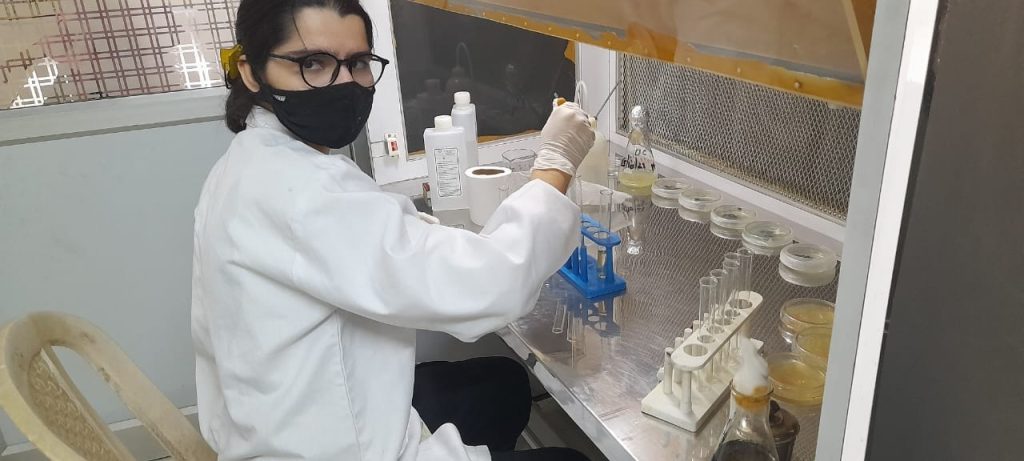
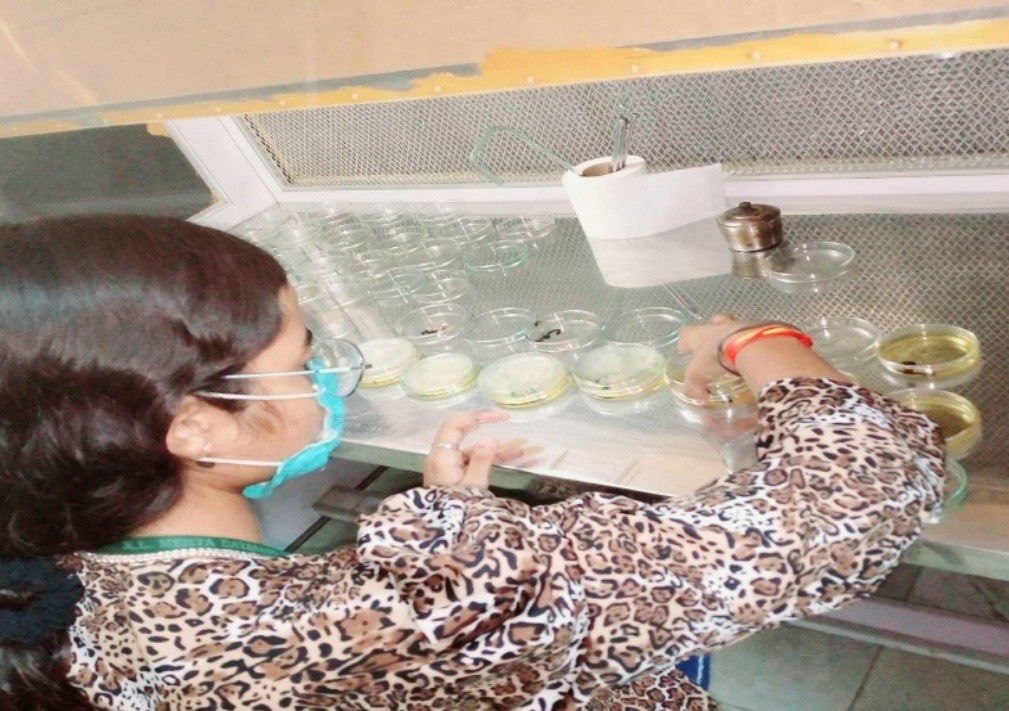


Outcome: Trichoderma species are prolific producers of Cellulase enzymes, which are crucial for the breakdown of cellulose into fermentable sugars. These enzymes are highly applicable in bioprocessing industries, such as biofuel production, pulp and paper manufacturing, and textile processing, to efficiently convert biomass into valuable products.
Our study analysed the significant role of fungal Cellulase enzyme in breaking down of Cellulose to obtain free fermentable sugars which were readily available for SHF. The study provided the enhanced bioprocessing and alcohol yield from waste biomass.





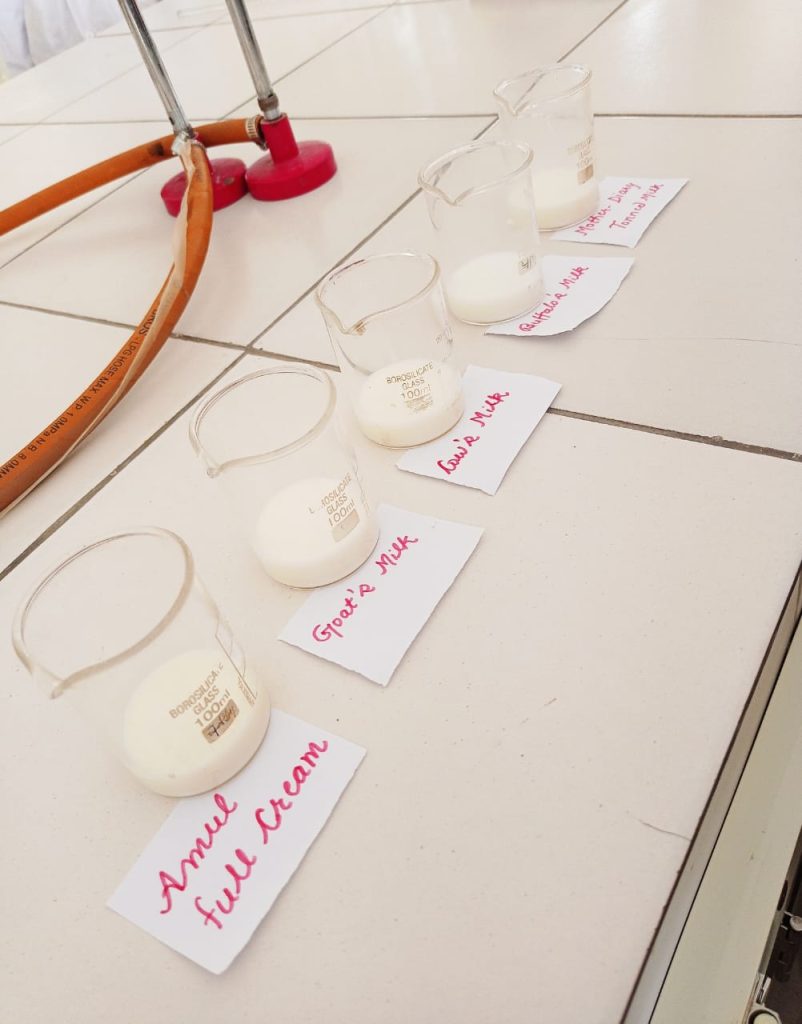
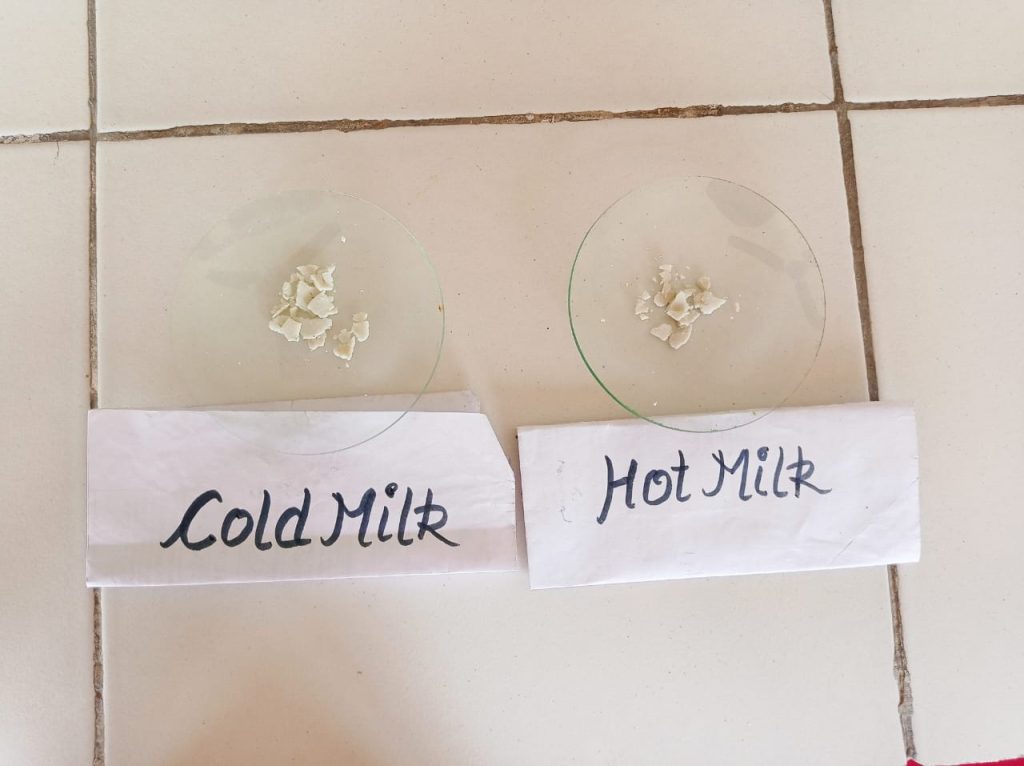
Outcome: The observations and calculations done for different milk samples explained that the goat milk contains the highest amount of casein in it while in case of packaged milk, toned milk has the highest amount of casein. Casein is the main protein constituent of milk and contains all the amino acids which the human body cannot manufacture on its own. More the casein present in the milk, the healthier the milk is. So, milk which is considered as a complete food should be consumed daily for better and health human growth.










Outcome: The designed work provided the four isolated soil borne fungal species. Isolated fungi were further characterized by the Microscopic & staining methods. The fungal mycelia & spores were observed for detailed morphological characters.
Advance study on isolated soil microbes can provide valuable information about microbial production of bioactive compounds like antibiotics and enzymes. Utilizing Specific or Assay media for Isolation uncovered their role in production of novel compounds.




